Unveiling the Average Cost of Insurance Per Month: A Comprehensive Guide
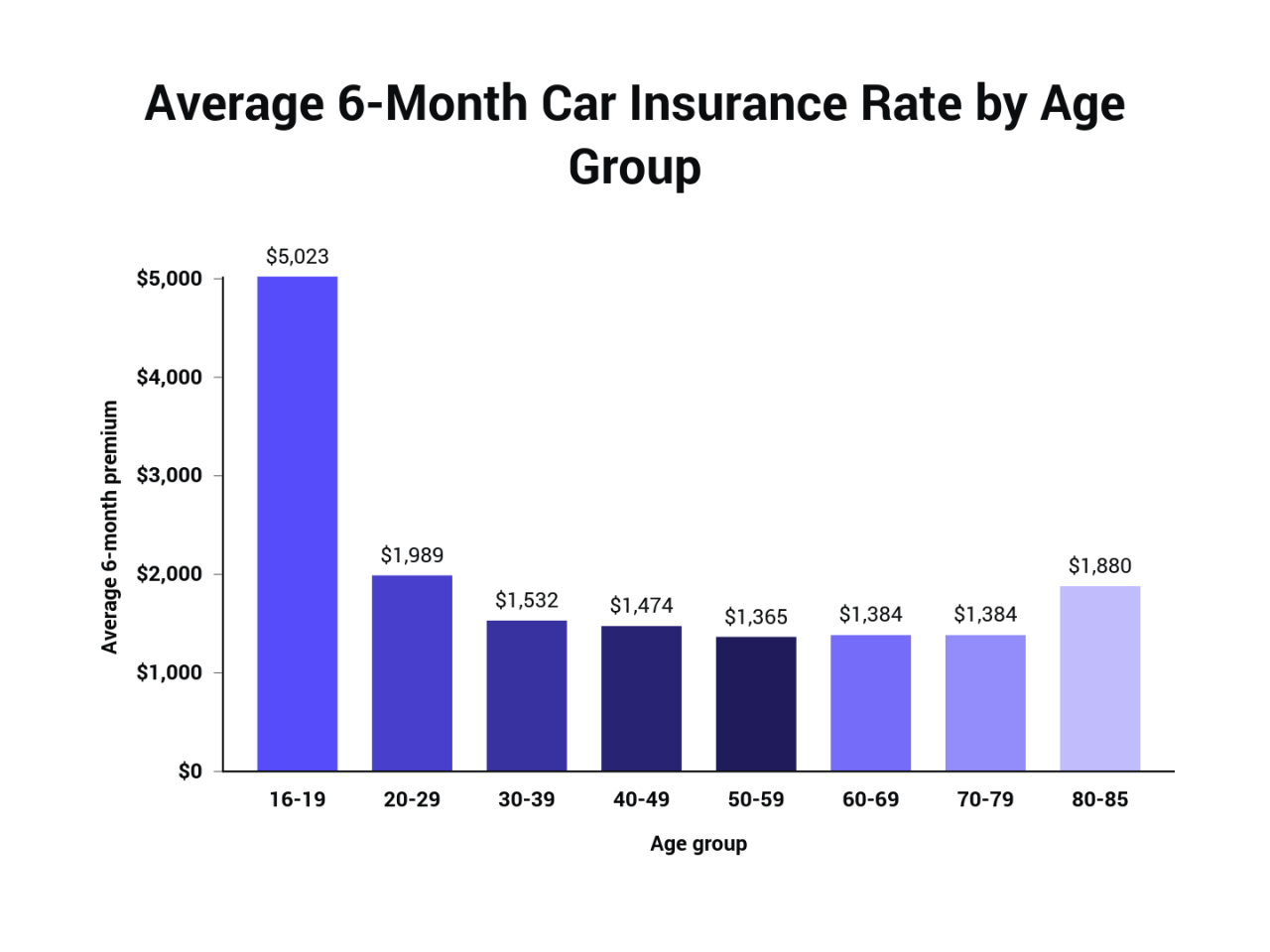
Insurance, an essential safeguard against life’s uncertainties, comes at a cost. Understanding the average cost of insurance per month is crucial for individuals and families seeking financial security. From auto to health, homeowners to renters, insurance premiums vary widely, influenced by a complex interplay of factors. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of insurance pricing, providing insights into the key drivers of costs and strategies for navigating the market effectively. By analyzing average costs across different insurance types, exploring regional variations, and examining cost trends, we aim to empower readers with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions about their insurance needs. We will also discuss strategies for minimizing premiums and highlight innovations shaping the insurance landscape. Understanding Insurance Costs Insurance premiums are the monthly payments you make to an insurance company in exchange for coverage against financial losses. These costs can vary widely, depending on several factors. Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions about your insurance needs and budget. Factors Influencing Insurance Costs The cost of insurance is influenced by a multitude of factors. These factors can be broadly categorized as: Risk Factors: These factors are related to the likelihood of an insured event occurring. Age: Older individuals are generally considered higher risk due to increased chances of health issues or accidents. Health: Individuals with pre-existing conditions may face higher premiums as they are statistically more likely to require medical care. Driving Record: A history of accidents, traffic violations, or DUI convictions can significantly increase auto insurance premiums. Location: Areas with higher crime rates or natural disaster risks may have higher insurance premiums. Policy Details: The specific features of your insurance policy can significantly impact the cost. Coverage Limits: Higher coverage limits, such as for medical expenses or property damage, generally result in higher premiums. Deductibles: A higher deductible, which is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before insurance kicks in, typically leads to lower premiums. Type of Coverage: Different types of insurance, such as health, auto, or home, have varying premium structures based on the specific risks involved. Company Factors: The insurance company itself plays a role in determining premiums. Financial Stability: Insurance companies with a strong financial history and a proven track record of paying claims may offer lower premiums. Competition: A competitive insurance market in your area can lead to lower premiums as companies vie for customers. Profitability: Insurance companies need to generate profits to stay in business. These profits are factored into premium calculations. Common Insurance Types and Cost Ranges Here’s a breakdown of common insurance types and their typical cost ranges: Health Insurance: Premiums vary widely depending on factors such as age, health, location, and coverage level. Average monthly premiums for individual health insurance plans in the United States can range from $400 to $1,000, but these costs can be significantly higher for families or individuals with pre-existing conditions. Auto Insurance: The cost of auto insurance depends on factors such as vehicle type, driving record, location, and coverage level. Average monthly premiums for auto insurance in the United States can range from $50 to $200 per month. Homeowners Insurance: Homeowners insurance premiums are influenced by factors such as the value of the home, location, and coverage level. Average monthly premiums for homeowners insurance in the United States can range from $50 to $200 per month. Renters Insurance: Renters insurance premiums are typically lower than homeowners insurance premiums, but they still vary based on factors such as the value of your belongings and the location of your rental property. Average monthly premiums for renters insurance in the United States can range from $10 to $50 per month. Insurance Premium Calculation Insurance premiums are calculated based on a complex formula that takes into account various factors. Premium = (Expected Losses + Operating Expenses + Profit Margin) / Number of Policyholders This formula essentially reflects the cost of covering expected claims, administrative expenses, and the insurance company’s profit margin, divided by the number of policyholders. Key Factors Influencing Premiums Insurance premiums are not a one-size-fits-all cost. Several factors influence how much you pay for your coverage, and understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions about your insurance plan. Age Age is a significant factor in determining insurance premiums, particularly for car insurance. Younger drivers, especially those under 25, are statistically more likely to be involved in accidents. This higher risk translates to higher premiums for young drivers. As drivers age and gain experience, their risk profile decreases, leading to lower premiums. Location The location where you live also plays a role in your insurance premiums. Urban areas with high traffic density and higher crime rates tend to have higher insurance costs compared to rural areas. This is because the likelihood of accidents and theft is generally higher in densely populated areas. Driving History Your driving history is a crucial factor that insurers consider when setting premiums. A clean driving record with no accidents or traffic violations will result in lower premiums. Conversely, a history of accidents, speeding tickets, or DUI convictions will significantly increase your premiums. Credit Score While it may seem counterintuitive, your credit score can also influence your insurance premiums. Insurers often use credit scores as a proxy for financial responsibility, and a good credit score can indicate a lower risk profile. A higher credit score can lead to lower premiums, while a poor credit score may result in higher premiums. … Read more